Table of contents
The concept of cryptocurrencies and how they work on blockchain.
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual tokens that use cryptography to secure transactions and control the creation of new units. They operate on a decentralized, distributed ledger called a blockchain, which is a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, linked and secured using cryptography.
In a cryptocurrency network, every transaction is broadcast to the network and verified by a network of nodes (computers) through a process called consensus. Once verified, the transaction is added to a block and the block is added to the blockchain. This creates an immutable record of all transactions on the network and ensures that the same cryptocurrency unit cannot be spent twice.
The decentralized nature of the blockchain means that there is no central authority controlling the currency, such as a central bank. Instead, the network is maintained by a network of nodes, each with a copy of the blockchain, and the rules of the network are enforced through code.
Cryptocurrencies can be used for various purposes such as making purchases, trading, or as an investment. Some of the most well-known cryptocurrencies include Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin.
It's important to note that while cryptocurrencies have the potential to offer several benefits, such as increased security and privacy, they also come with risks, such as price volatility and the potential for hacking or scams. As with any investment, it's important to thoroughly research and understand the potential risks and rewards before investing in cryptocurrencies.
Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency, without a central bank or single administrator, that can be sent from user to user on the peer-to-peer bitcoin network without the need for intermediaries. It was created in 2009 by an unknown person or group of people using the name Satoshi Nakamoto and has since gained widespread popularity and controversy.

Bitcoins are created as a reward for a process known as mining. They can be exchanged for other currencies, products, and services. As of February 12, 2023, the current price of one bitcoin is approximately USD 48,000.
While bitcoin has been touted as a revolutionary technology that could change the way we think about money, it has also been criticized for its association with illegal activities and lack of regulation. Nevertheless, it has been adopted by a growing number of individuals, businesses, and financial institutions, and its popularity shows no signs of slowing down.
Ethereum
Ethereum is a decentralized, open-source, blockchain-based platform that enables the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications (Dapps). It was founded by Vitalik Buterin in 2014 and has since become one of the largest and most widely used blockchain platforms in the world.
Like Bitcoin, Ethereum is a cryptocurrency and its native token is called Ether (ETH). Ether is used to pay for transactions and computational services on the network. In contrast to Bitcoin, which was designed primarily as a digital currency, Ethereum was created to provide a platform for decentralized applications that can automate the execution of complex tasks.

Ethereum has several features that make it different from other blockchain platforms, including its ability to support smart contracts, its use of a virtual machine (Ethereum Virtual Machine) that executes code on the network, and its support for decentralized applications.
As of February 12, 2023, the current price of one Ether is approximately USD 1,550. Ethereum has a large and growing community of developers and users, and it is widely considered to be a leader in the blockchain space, with several exciting developments planned for the future.
Public and Private blockchains
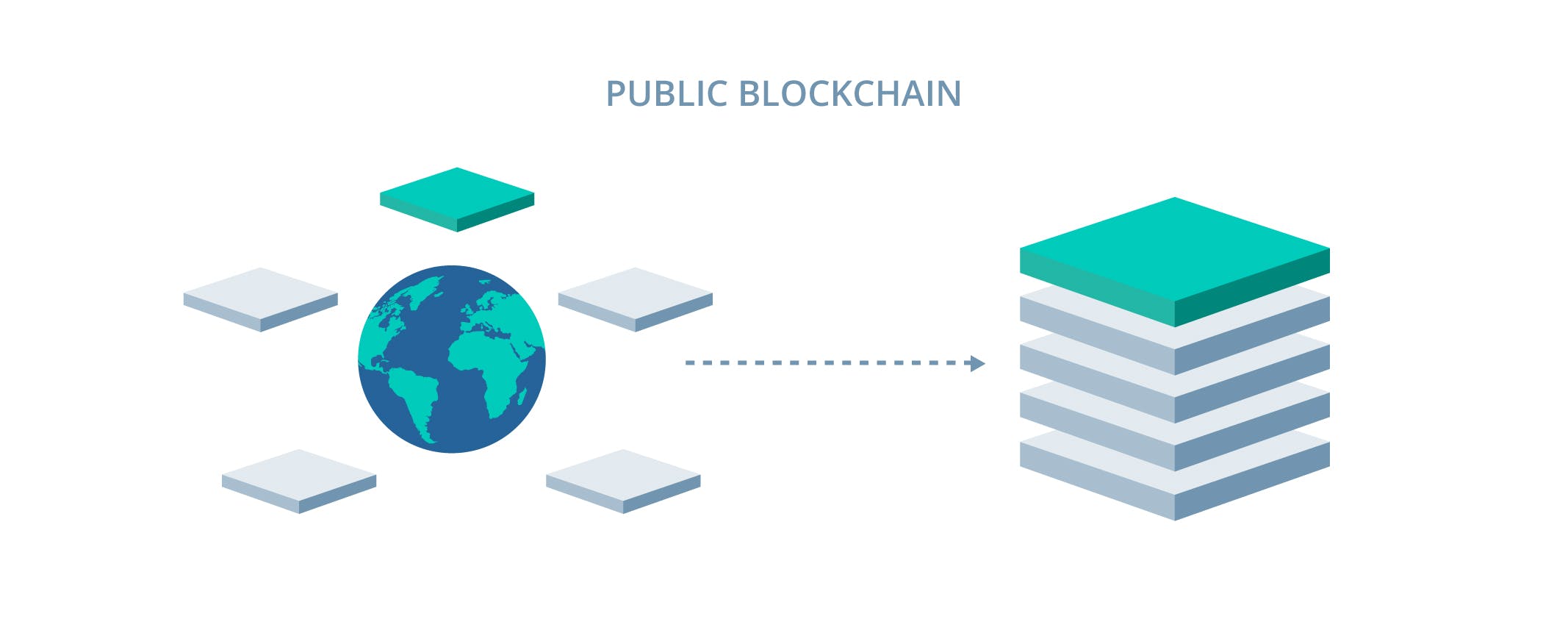
Public Blockchain
A public blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that is open to anyone who wants to participate. In a public blockchain, anyone can join the network, validate transactions, and add new blocks to the chain. Public blockchains are typically characterized by their openness, transparency, and decentralization, and they allow for secure, peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a trusted third party.
Public blockchains are often used for cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, where anyone can participate in the network and participate in the verification of transactions. These networks are also often used for decentralized applications and smart contracts, which allow for complex transactions to be automated and executed securely and transparently.
One of the key features of public blockchains is that they are maintained by a network of nodes, each with a copy of the ledger. This helps to ensure the security and integrity of the network, as any changes to the blockchain must be verified by a consensus of nodes.
It's important to note that while public blockchains offer many benefits, such as increased security and transparency, they can also be vulnerable to issues such as scalability and performance, as well as the potential for malicious actors to engage in activities such as hacking and spamming. As with any technology, it's important to understand the risks and limitations of public blockchains, as well as their potential benefits.
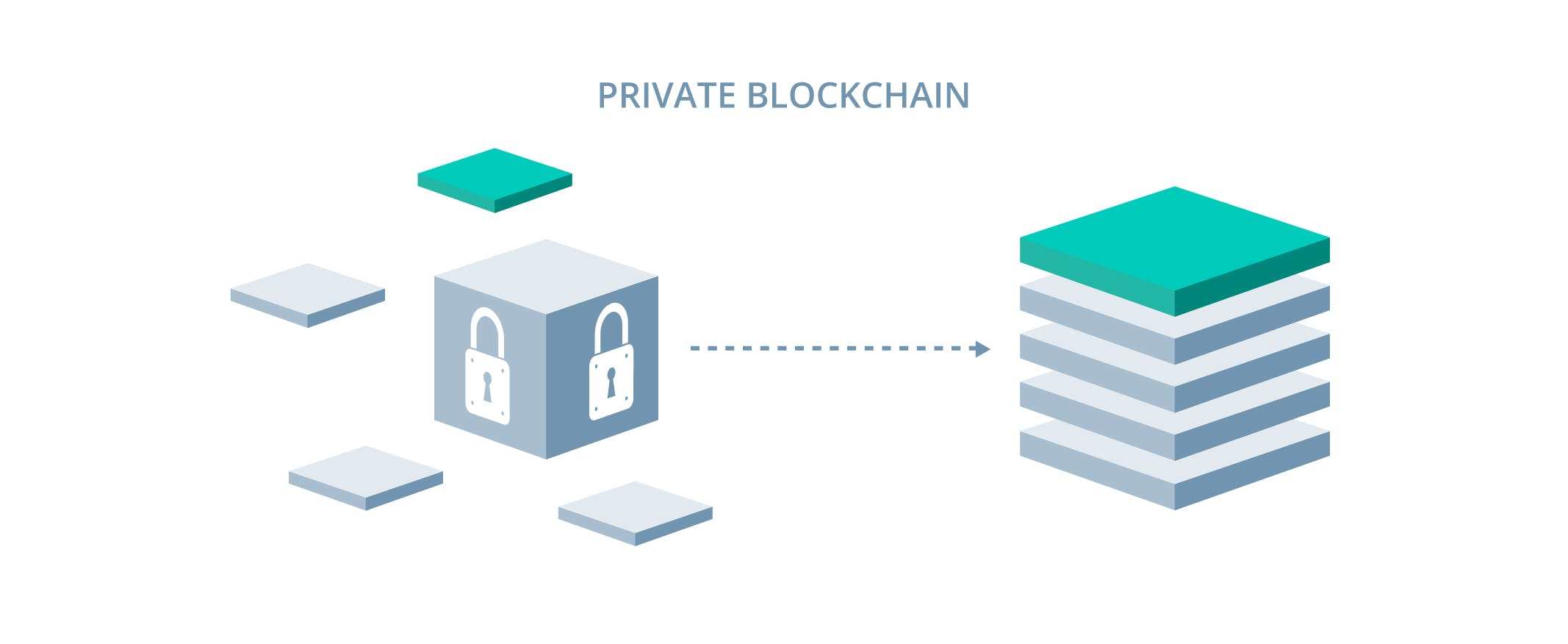
Private Blockchain
A private blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that is restricted to a specific group of participants. Unlike public blockchains, private blockchains are not open to everyone and access is controlled by the network administrator.
Private blockchains are often used in businesses and organizations where there is a need for a secure and transparent record of transactions, but where access needs to be restricted to a specific group of participants. For example, a company might use a private blockchain to keep track of supply chain transactions, or a financial institution might use a private blockchain to securely and transparently record transactions between its customers.
In a private blockchain, the network administrator can control access to the network, set the rules for transactions, and determine who can validate transactions and add new blocks to the chain. This allows for a high degree of customization and control, but also means that the network is not as decentralized as a public blockchain.
Private blockchains typically offer improved performance and scalability compared to public blockchains, as they have a smaller number of nodes and are designed for specific use cases. However, they also come with some limitations, such as a reduced level of security and decentralization, as well as a potential for a single point of failure if the network administrator is compromised.
In summary, private blockchains are decentralized, distributed ledgers that are restricted to a specific group of participants and offer improved performance and scalability compared to public blockchains. They are often used in businesses and organizations where access needs to be controlled, but they also come with some limitations, such as reduced security and decentralization.
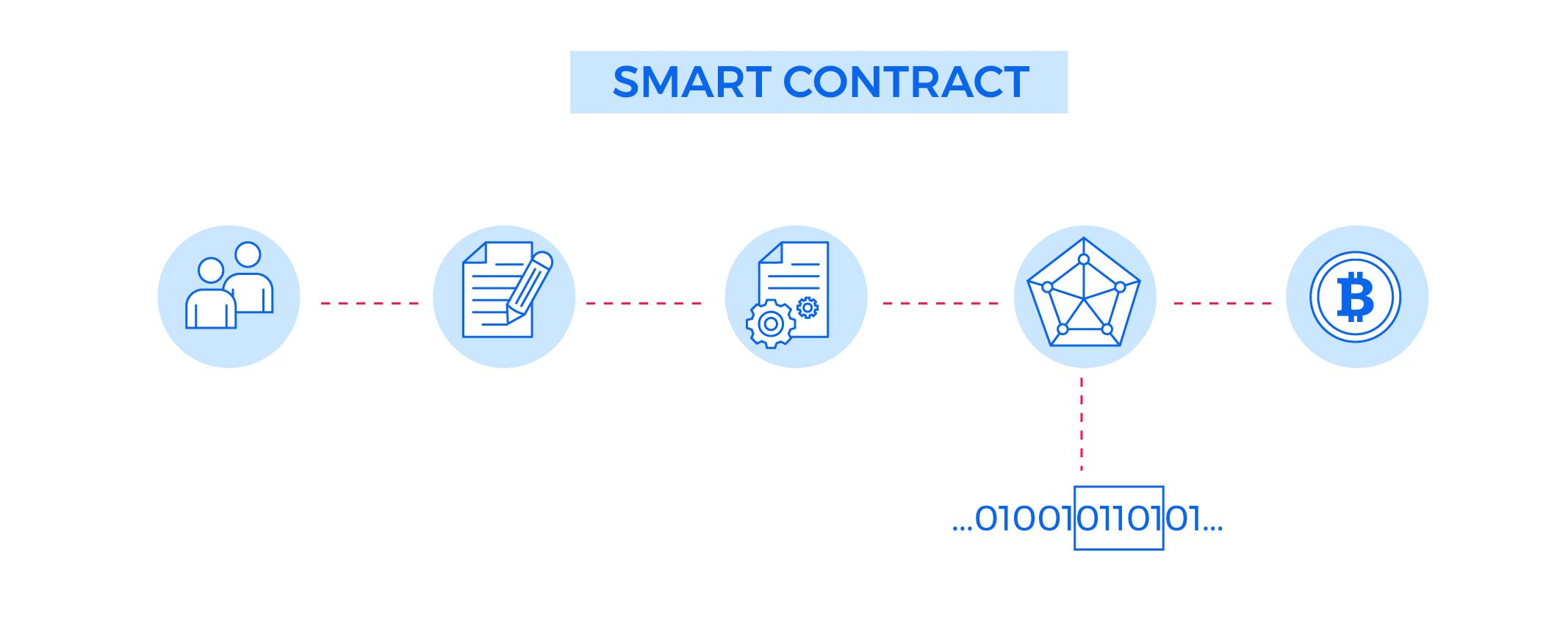
The Role of Smart Contracts in Blockchain Technology
What are Smart Contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. They are an essential component of blockchain technology and they play a critical role in enabling secure, transparent, and decentralized transactions.
How do Smart Contracts Work?
In a blockchain network, smart contracts are stored on the blockchain and are executed automatically when certain conditions are met. Once a smart contract is deployed to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring that the terms of the agreement are enforced in a secure and tamper-proof manner.
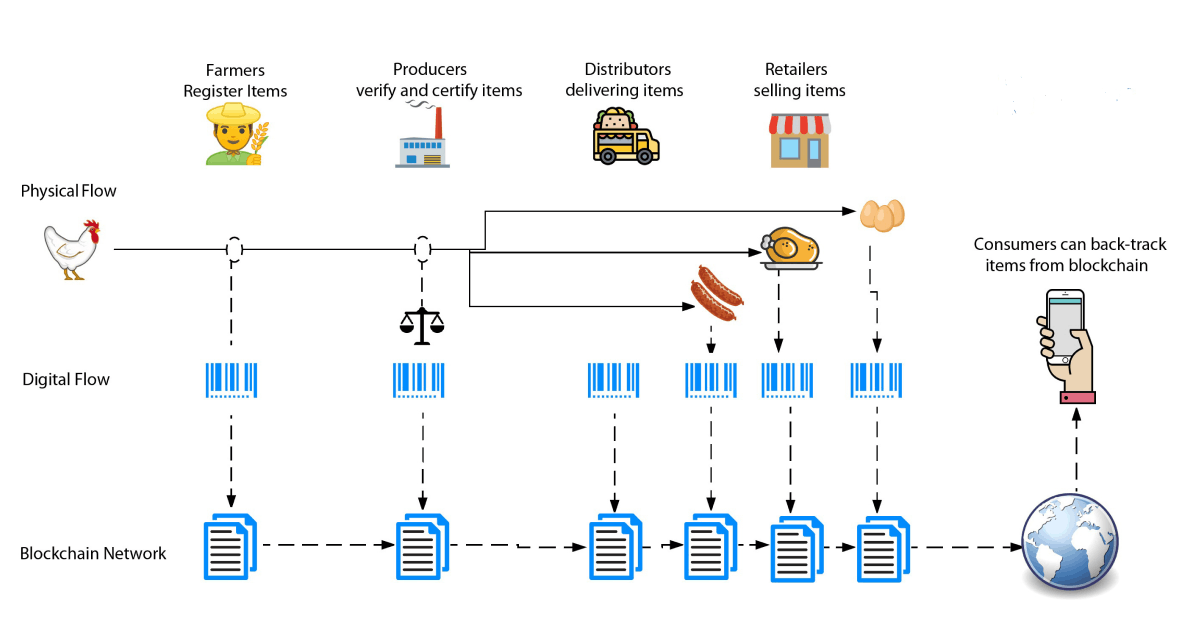
The use of smart contracts in blockchain technology can have numerous applications, ranging from financial transactions to supply chain management. For example, in a financial transaction, a smart contract can automatically transfer funds from the buyer to the seller when a certain condition is met, such as the delivery of a product or the expiration of a certain date.
In supply chain management, a smart contract can be used to track the movement of goods and enforce rules and conditions throughout the supply chain. For example, a smart contract could automatically release payment to a supplier when a shipment is delivered and received, without the need for manual intervention.
Smart contracts also play a key role in enabling decentralized applications (dApps) and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). dApps are applications that run on a blockchain network and use smart contracts to automate complex transactions, while DAOs are organizations that are run by code, without the need for a central authority.
In conclusion, smart contracts are an essential component of blockchain technology and they play a critical role in enabling secure, transparent, and decentralized transactions. They can be used in a wide range of applications, from financial transactions to supply chain management, and they are a key enabling technology for decentralized applications and decentralized autonomous organizations.
The potential benefits and limitations of blockchain technology
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way that information is stored, transmitted, and processed, offering numerous benefits across a wide range of industries and applications.
Pros
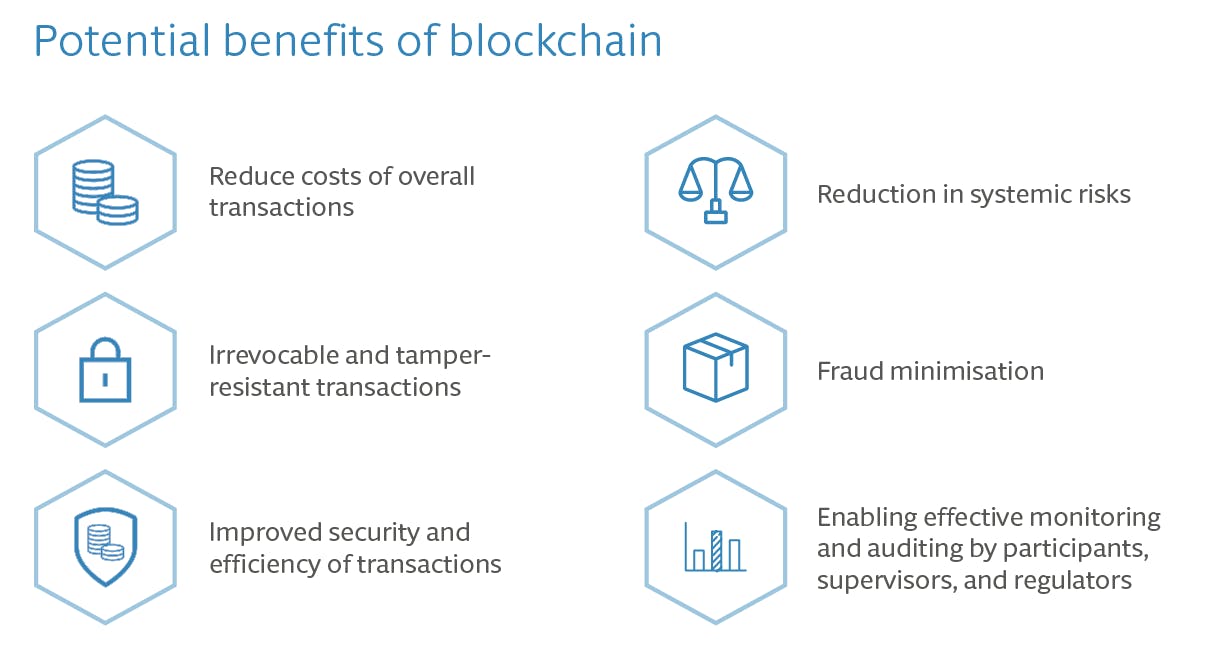
Some of the key potential benefits of blockchain technology include:
Increased Security: Blockchain technology is highly secure due to its decentralized and distributed nature, as well as its use of cryptographic algorithms. This makes it more difficult for hackers to penetrate the network and steal or manipulate data.
Transparency: Blockchain technology allows for transparency in transactions, as all participants in the network have access to an up-to-date and tamper-proof record of all transactions.
Decentralization: Blockchain technology is decentralized, meaning that it operates without a central authority. This reduces the risk of a single point of failure and makes it more resistant to censorship and control.
Improved Efficiency: By automating processes and reducing the need for intermediaries, blockchain technology can increase efficiency and reduce costs in many industries.
Traceability: Blockchain technology allows for the creation of tamper-proof records, enabling the tracing of assets and information throughout their lifecycle.
Cons
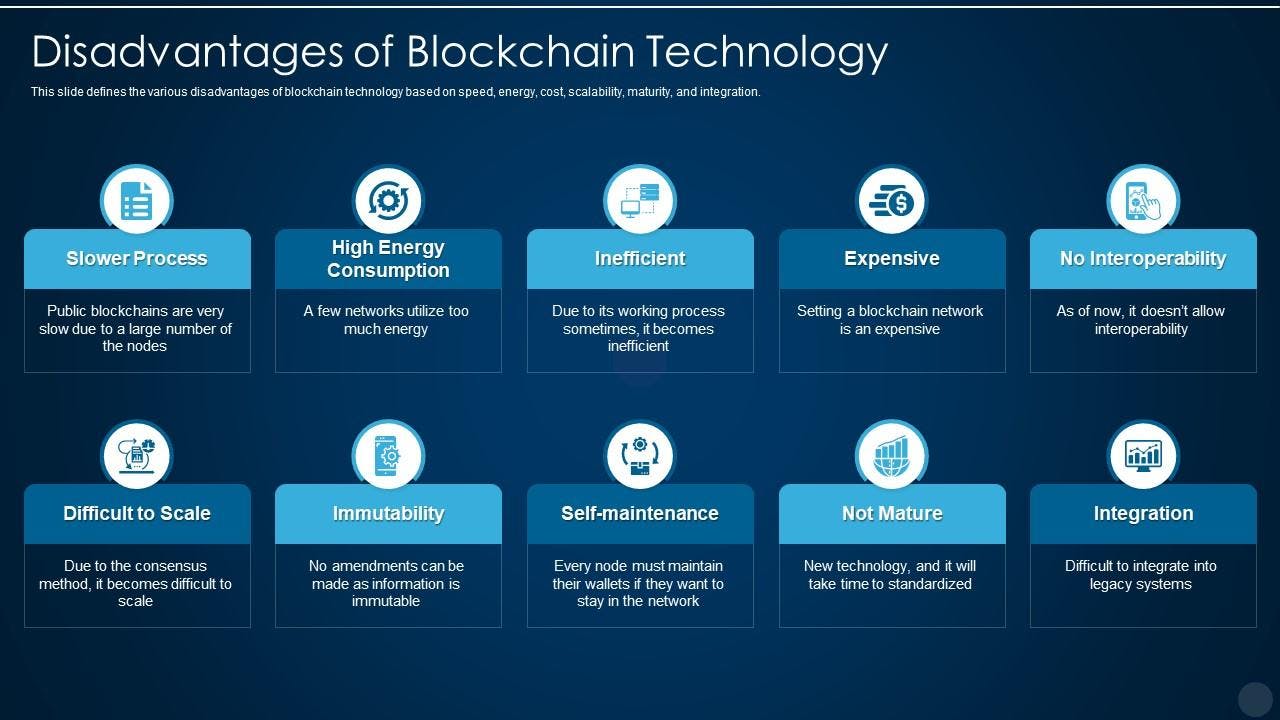
However, blockchain technology also has some limitations that must be considered, including:
Scalability: The current state of blockchain technology is not yet able to handle the large number of transactions required for widespread adoption in many industries.
Regulation: Blockchain technology operates outside of traditional regulatory frameworks, which can be a challenge for governments and organizations looking to adopt the technology.
Complexity: The technical complexity of blockchain technology can make it difficult for non-technical users to understand and use.
Energy consumption: The current consensus mechanisms used in most blockchain networks, such as proof of work, can be highly energy-intensive and environmentally damaging.
Adoption: Widespread adoption of blockchain technology requires significant changes in the way that businesses and individuals operate, which can be a challenge.
In conclusion, blockchain technology offers numerous potential benefits, including increased security, transparency, decentralization, and efficiency. However, it also has some limitations, including scalability, regulation, complexity, energy consumption, and adoption. It's important to carefully consider these benefits and limitations when deciding whether and how to adopt blockchain technology.
The future of blockchain and its potential impact on various industries
The future of blockchain technology is highly uncertain, but it has the potential to greatly impact a wide range of industries.
Here are a few of the industries that may be most affected by blockchain technology in the future:
Financial Services: Blockchain technology has the potential to transform the financial services industry by enabling secure and transparent financial transactions, reducing the need for intermediaries, and improving the efficiency of financial processes.
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain technology can be used to create tamper-proof records of transactions in supply chains, allowing for greater transparency and traceability of goods and reducing the risk of fraud and counterfeiting.
Healthcare: Blockchain technology can be used to securely store and manage sensitive healthcare information, improving the privacy and security of patient data and enabling more efficient sharing of information between healthcare providers.
Real Estate: Blockchain technology can be used to create tamper-proof records of property ownership and transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and increasing the efficiency of real estate transactions.
Government: Blockchain technology has the potential to improve the efficiency, transparency, and security of government processes, such as voting and record keeping.
Internet of Things (IoT): Blockchain technology can be used to secure and manage transactions between IoT devices, enabling new forms of automation and improving the security of IoT networks.
It's important to note that the impact of blockchain technology on these and other industries will depend on many factors, including the speed of technological advancements, regulatory developments, and market adoption.
In conclusion, the future of blockchain technology is highly uncertain, but it has the potential to greatly impact a wide range of industries, including financial services, supply chain management, healthcare, real estate, government, and the Internet of Things. The exact impact of blockchain technology will depend on several factors and will likely evolve.
Conclusion
As the world of blockchain technology continues to evolve, Ethereum and its native cryptocurrency, ETH, have emerged as some of the most promising innovations in the space. In the next article, we will take a closer look at Ethereum and the Ethereum Blockchain, exploring the underlying technology, its unique features, and its potential applications in a variety of industries. From smart contracts to decentralized finance, the possibilities with Ethereum are endless, and we are excited to explore them in more detail in further articles. Stay tuned!
I hope the information provided was helpful and informative. If you have any further questions or need clarification, feel free to leave a comment or reach out to me through Twitter or LinkedIn. It would be great to connect and continue the conversation.
👋Thank you for taking the time to read this article. Until next time!
Don't forget to Subscribe Newsletter...

